What is Solid State Drive (SSD) and how does it work?
Solid State Drive is one of a variety of permanent storage memory. Unlike common hard disk memory, a piece cannot be found in the Solid State Driver (SSD) that is on the go. Follow us to learn more about this memory and how it works.
What does the word SSD mean?
The word SSD stands for Solid State Drive, meaning "solid state drive". The first SSD was used in IBM's supercomp computers from 1970 to 1980. The solid state disk is also known by the following names:
- Solid State Drive
- Non-permanent memory (permanent memory)
- Electronic Drive (Electric Drive)
- Flash-based Disk (disk by flash design)
- SSD (SSD)
What is a solid state drive?
A solid state drive (SSD) is one of a variety of permanent reading and writing memory that is designed based on flash chips.
Unlike hard drives (which use magnetic loads to store data), solid-state drives store their data in very small semiconductor chips that exist inside its chips. The average rate of direct access to each data storage location in this type of memory is 0.1 milliseconds (equal to 0.001 seconds) and the data transfer speed is usually between 70 and 600 MB/s.
Usually, such memory uses standard SLC technology (abbreviated single-level cell, meaning "single-stage cell"), which allows each cell (storage space in SSD) to store only two values (fill or empty – one bit).
In some other types of SSD memory that have used MLC technology (abbreviation multi-level cell meaning "multi-stage cell"), cells can store four different mode types, in which case, memory can store twice as much data than SLC memory.
What is the task of solid state drive?
Like other permanent and lateral memory, solid state drives (SSD) also have a task, which is to maintain data permanently.
What are the features and benefits of solid state drive?
It retains data in SSD memory unlike RAM even when no power supply is connected to it.This type of memory has no moving parts and therefore operates almost without sound. This feature is one of the reasons why today's laptops use SDD instead of HDD.The speed of reading and writing is much higher compared to HDD, and its energy consumption is far less.
In summary, solid state drives have superior features and characteristics over hard drives, including:
- Resistant to blows
- High speed of reading and writing
- Less energy consumption
- Almost no fuss
- SSD memory does not require defragment (read data writing section)
- Unlike hard drives, they are resistant to shock and vibrate.
- These types of memory usually don't generate much heat.
These same features make solid-state drives superior and more optimized than hard drives. So they usually use SDD on newer computers instead of HDD memory.
What are the disadvantages of solid state drive?
Although these types of memory have many advantages, the disadvantages should not be passed on:
- The cost of these types of memory is high compared to hard drives. So users prefer hard drives to SSDs.
- Cells have a lifespan that is reduced by each "written" load. (Of course, this is one of the disadvantages of all electrical components) drive cells that use SLC technology can usually be written from 50,000 times to 100,000 times. Cells on drives that use the MLC standard can be written between 3,000 and 5,000 times. Of course, this is managed by the Controller and the solid state drive can work normally with this limitation for many years.
Note: The solid state drive built on DRAM does not have a "write cells" limit.
How does the solid state disk work?
How SSD memory works is based on semiconductor chips and chips.
A very large number, albeit with a very small size of transistors (also called cells), are tasked with data retention.
-
Solid state drive with Single-Level Cell standard
Each cell (transistors) stores data by holding or not. This means that each cell can only store one bit (zero or one).
 mode
mode
-
Solid state drive with Multi-Level Cell standard
In this standard, each cell can save two bits. This means that each cell can hold four different states. These modes are 00, 01, 11, 10 (binaryly) 
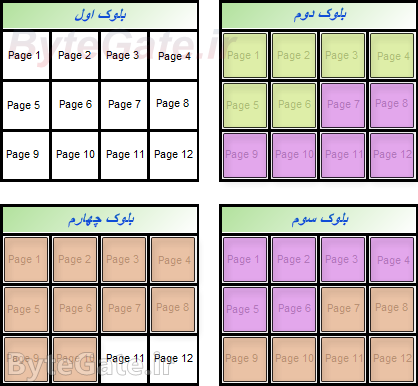
(The space scale is larger) each byte of the file is stored on one of the first pages of the empty block:
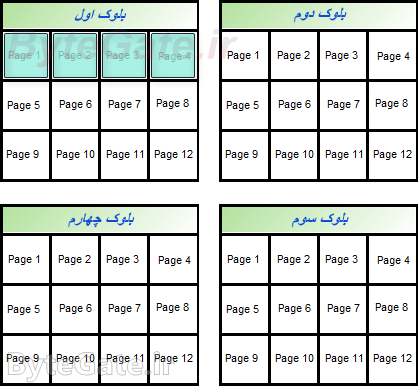
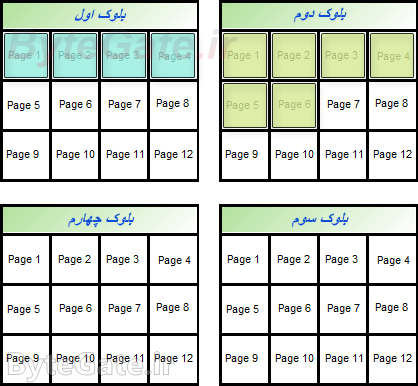
Now consider another file with a size of 8 KB:
We also store this 8-byte file on memory:
You can see that the pages associated with the second file are located next to the pages of the first file (note that in the main process, the data of the files is stored in separate clusters. See file system mail for more information):
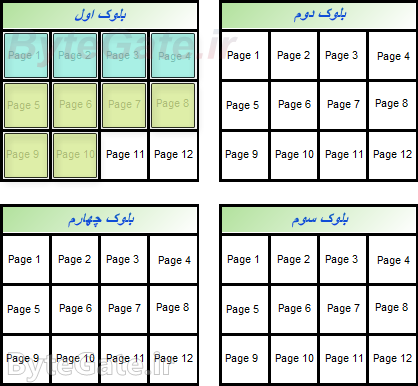
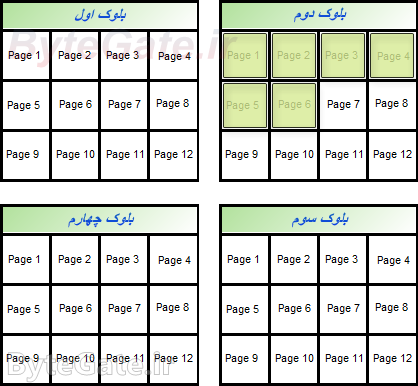
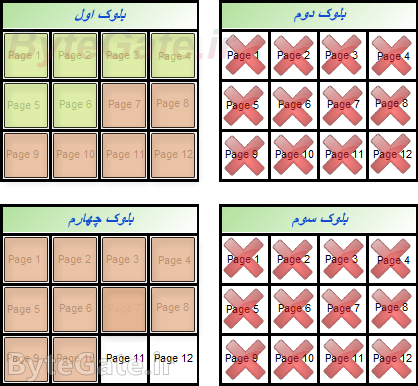
Now we want to delete a file from the drive memory. Because the solid state drive controller can't delete pages one by one, you'll need to clear the blocks associated with it altogether to delete a value (e.g. first file data).
Because we're just going to delete the first file, so the data from the second file (which we don't want to erase) will be moved to the next blank block:
In this case, only the first file data are in a block, and the controller can easily delete the first file data by deleting the whole first block:
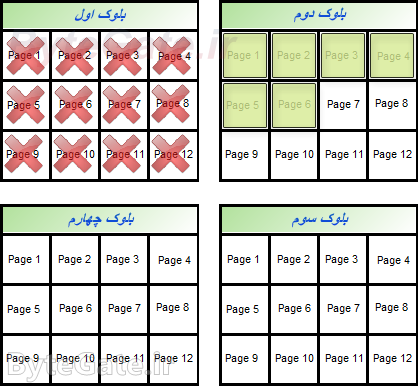
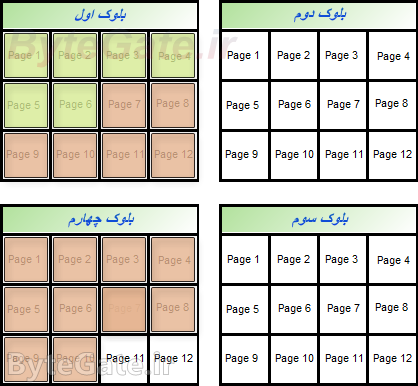
You will see that the entire first block has been removed:
Now we're going to save several more files on memory.
We save a 12-bit file:
You'll see the controller stores data after the last page is filled.
Then we save another file with a size of, for example, 16 bits:
Now you can see the makeup of three files in a solid state drive (SSD).
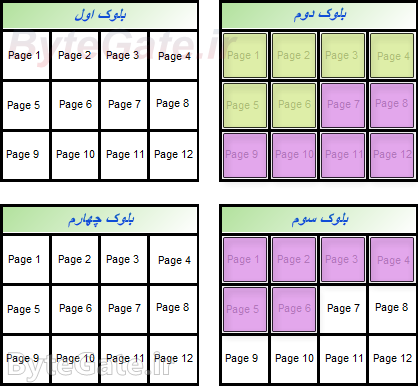
If we want to delete the second file (purple), we need to leave all of its data in the blocks alone. So we move the data that comes with the third file data in a block to a blank block (or the end of the block with a blank):
Now the controller clears the second and third blocks altogether:
You can see that the third file (purple) is completely deleted and the other files are in place:
How to write data in SSD memory is how you viewed it. Of course, as mentioned above, scales have changed for ease of work and better understanding.
Read data from solid state drives:
Reading data is not as difficult as writing or modifying it. The controller has direct access to the desired data, so it can easily extract the data and return them as an output.
Some SSD manufacturers
In this section, some of the most important manufacturers of SSD drives are listed as: